Healthcare-associated Infections (HAIs) Represent a Major Threat to Patient Safety and Public Health
1 IN 31
hospital patients will experience at least one HAI2
$43,000
in incremental costs per patient1
72,000
deaths in the US annually2
$28-45B
in estimated direct medical costs in the US annually3


Identification service for clinically relevant bacterial and fungal isolates

Custom project work with our world-class team of scientists
epiXact® HAI
Taking outbreak investigations to the next level
Single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) based analysis of genomic distance is the most precise and definitive way to conduct an outbreak investigation. EpiXact HAI gives you the confidence to act quickly when an outbreak is real and to call off unnecessary and expensive interventions when an outbreak can be ruled out.
With epiXact HAI you can:
- Determine outbreak cluster inclusion/exclusion of sample with superior resolution to most methods
- Receive a conclusive report within 2 days
- Conduct a personal consultation with our bioinformatics experts
Day Zero Diagnostics is a CLIA certified laboratory. EpiXact HAI is available as a CLIA validated service or Research Use Only. EpiXact HAI is available as Research Use Only in CA, MD, PA, RI and NY.

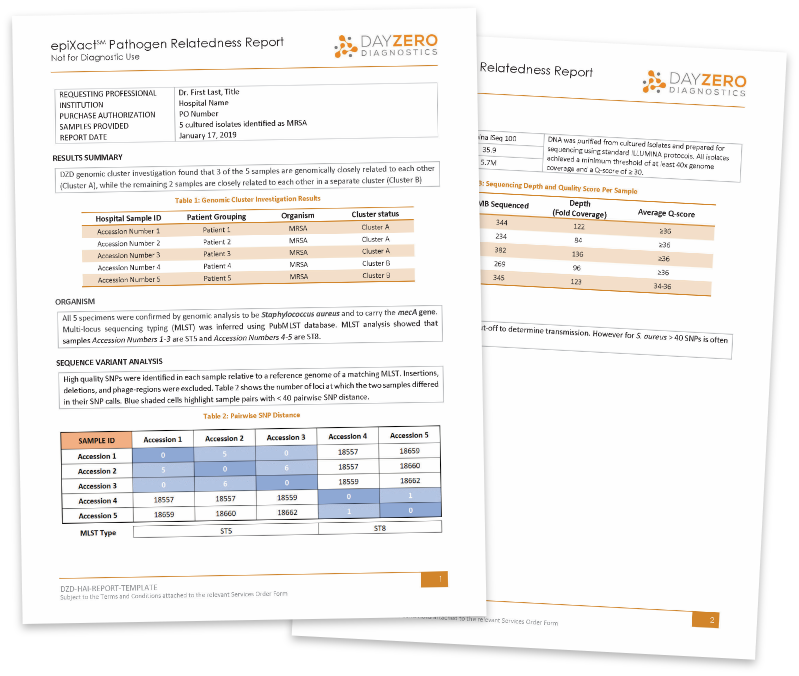
Sample Report
With epiXact HAI’s whole-genome SNP analysis, we identify differences at the single DNA base pair level to estimate genomic distance between samples.
Each report includes:
- Simple, easy to read report with actionable interpretation
- Confirmation of organism ID and MLST typing
- SNP analysis and distance matrix visualization of relatedness
- Determination of outbreak cluster inclusion/exclusion for each sample
- Sequencing quality metrics including genome coverage and Q-score


epiXact® ID
Comprehensive characterization of clinically relevant bacterial and fungal isolates via ONT sequencing
EpiXact ID, our species agnostic identification and characterization service utilizes the un-matched resolution of WGS, specifically ONT long-read sequencing, to deliver with rapid turnaround times. This service uses ONT sequencing for rapid turnaround times.
Providing:
- Species & strain identification & subtyping
- Resistance genes profiling including Keynome® gAST a proprietary AI-based prediction model
- Phylogenomic analysis for populations (>10 samples) and clade identification and grouping for comparative genomics


epiXact® PRO
Building custom pipelines for complex or high sample volume projects
Whether you have a cohort of samples that needs sequencing, are working on a research project, or have any other need that requires building a custom computational biology pipeline, our world-class team of scientists is available for your needs.
This service includes short read or long read sequencing (using Illumina and Oxford Nanopore sequencers), tailored depending on your project requirements and research needs.
Providing:
- Transmission analysis at scale to detect transmission pathways and perform large-scale surveillance
- Metagenomic profiling to detect species and abundance rates
- Genomic characterization, including species determination and typing, resistance and virulence genes, plasmid profile
Collaborating with Biotech and Pharma for Custom Assay Development
Day Zero Lab partners with biotech and life science companies to leverage our expertise in whole-genome sequencing, computational biology, and laboratory testing to develop a custom assay to fit your specific therapeutic need. Development of new assays is guided by our world-class team of scientists and in compliance with the Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments (CLIA).
Sign-Up to Receive the Monthly SNPIT Newsletter
References:
1. Ward et al. Integration of genomic and clinical data augments surveillance of healthcare-acquired infections. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2019;40: 649–655. doi:10.1017/ice.2019.75
2. Healthcare-associated Infections. In: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2020 p. Accessed 7/7/2020.
3. Scott R. The direct medical costs of healthcare-associated infections in US hospitals and the benefits of prevention. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 2009.